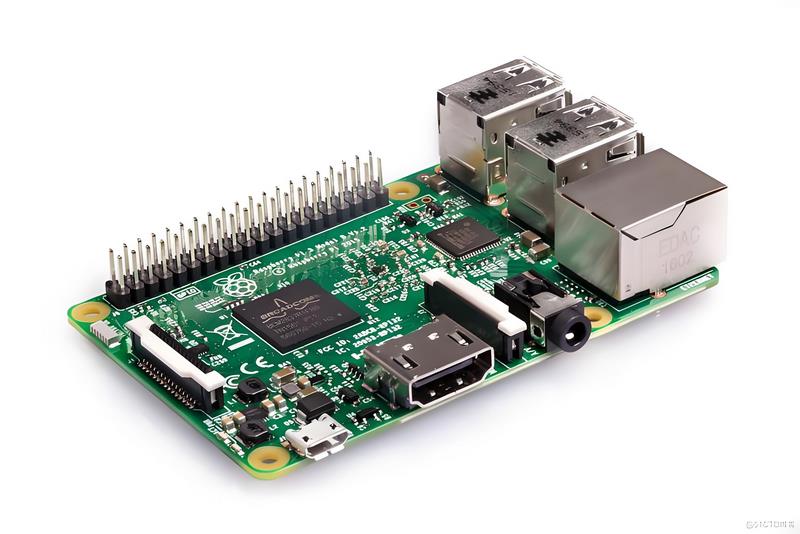
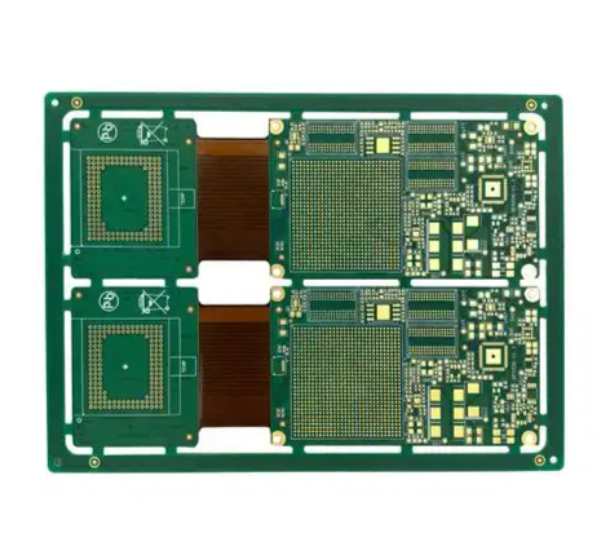
Ask For A Quick Quote
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your email.
Request a Sample
With the mission of “Smart Manufacturing - Global Delivery”, we help our customers shorten the time-to-market and optimize the supply chain cost through continuous technology iteration and digital upgrading. We look forward to working with you to define the future of electronic manufacturing!
- Technology Driven Intelligent Manufacturing
- Full-process quality control
- In-depth industry experience
- Agile Service Network
Navigating the Complexities of PCB Assembly with Precision Instruments
2026-01-07
Navigating the Complexities of PCB Assembly with Precision Instruments
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding PCB Assembly
- 2. The Role of Precision Instruments in PCB Assembly
- 3. Key Components of PCB Assembly
- 4. PCB Design Considerations for Successful Assembly
- 5. Precision Instrumentation Techniques
- 6. Best Practices in PCB Assembly
- 7. Troubleshooting Common PCB Assembly Issues
- 8. The Future of PCB Assembly and Precision Instruments
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Assembly
- 10. Conclusion
1. Understanding PCB Assembly
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) assembly is a critical process in electronics manufacturing that involves the integration of electronic components on a board to create functional devices. This process requires meticulous attention to detail and sophisticated tools, as even minor errors can lead to significant malfunctions. The assembly process typically includes several stages, such as surface mount technology (SMT), through-hole mounting, soldering, and inspection. Understanding each of these stages is imperative for achieving high-quality results.
What is PCB Assembly?
PCB assembly is the process where various electronic components are connected to a circuit board, allowing for the creation of complex electronic systems. This includes everything from smartphones and computers to medical devices and automotive electronics. Efficient PCB assembly is crucial for the performance and reliability of the final product.
The Importance of Quality in PCB Assembly
Quality assurance in PCB assembly is fundamental. The use of precision instruments during assembly not only enhances the accuracy of component placement but also minimizes defects. High-quality PCB assemblies lead to improved performance, reduced costs, and decreased time-to-market for electronic products.
2. The Role of Precision Instruments in PCB Assembly
Precision instruments are essential tools in PCB assembly. They ensure that each component is placed with exactitude and that connections are made correctly. These instruments include soldering machines, placement robots, inspection equipment, and testing devices. Their integration into the assembly process greatly influences the overall success of the PCB manufacturing workflow.
Types of Precision Instruments Used in PCB Assembly
Several types of precision instruments play pivotal roles in PCB assembly:
- **Pick and Place Machines**: These automated devices are responsible for accurately positioning components onto the PCB. Their speed and precision significantly enhance assembly efficiency.
- **Soldering Equipment**: This includes both manual and automated soldering machines that ensure reliable electrical connections between components and the PCB.
- **Inspection Tools**: Visual inspection systems, such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), check for defects in solder joints and component placement.
- **Testing Instruments**: These instruments verify the functionality of the assembled PCBs through rigorous testing procedures.
3. Key Components of PCB Assembly
Understanding the various components involved in PCB assembly is critical for delivering high-quality products. Key components include:
Basic Components
- **Resistors**
- **Capacitors**
- **Diodes**
- **Integrated Circuits (ICs)**
- **Connectors**
Advanced Components**
As technology evolves, new components emerge, such as:
- **Microcontrollers**
- **RFID Tags**
- **Sensors**
These components often require specialized handling and assembly techniques, emphasizing the need for precision instrumentation.
4. PCB Design Considerations for Successful Assembly
Effective PCB design is the foundation of successful assembly. Several factors must be considered during the design phase:
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
DFM principles ensure that PCBs are designed in a manner that facilitates efficient manufacturing and assembly. This includes considerations for component spacing, pad size, and solder mask design.
Design for Testability (DFT)
DFT focuses on creating PCBs that can be easily tested once assembled. This involves planning for test points and ensuring accessible connections.
5. Precision Instrumentation Techniques
Employing advanced techniques in PCB assembly can significantly enhance the precision and efficiency of the process.
Automated Processes
Automation plays a crucial role in modern PCB assembly. Automated systems allow for increased speed and consistency in tasks such as component placement and soldering.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
SPC involves the use of statistical methods to monitor and control the PCB assembly process. This technique helps identify variations and ensures that the manufacturing process stays within defined limits.
6. Best Practices in PCB Assembly
Implementing best practices in PCB assembly can dramatically improve the quality of the final product.
Regular Maintenance of Equipment
Ensuring that precision instruments are regularly calibrated and maintained is vital for consistent performance.
Employee Training
Investing in employee training programs ensures that staff are well-versed in using precision instruments and following assembly guidelines.
Quality Control Checks
Routine quality control checks throughout the assembly process help catch potential defects early, saving time and resources.
7. Troubleshooting Common PCB Assembly Issues
Despite best efforts, issues may arise during PCB assembly. Understanding common problems can help in swiftly addressing them.
Common Defects
- **Inadequate Solder Joints**: Caused by improper soldering techniques.
- **Misalignment of Components**: Typically results from issues with pick and place machines.
- **Electrical Failures**: Often due to design flaws or poor-quality components.
Strategies for Troubleshooting
- Implementing regular inspections and employing statistical process control can help quickly identify and resolve issues as they arise.
8. The Future of PCB Assembly and Precision Instruments
The landscape of PCB assembly is continuously evolving. As technology advances, so will the complexity of PCB designs and the precision instruments used.
Emerging Technologies
- **3D Printing**: This technology offers new opportunities for creating custom PCB designs and components.
- **Artificial Intelligence (AI)**: AI can optimize the PCB assembly process by predicting potential issues and suggesting improvements.
The Impact of IoT on PCB Assembly
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming how PCBs are assembled. With connected devices, real-time monitoring and control can enhance efficiency and responsiveness in the assembly process.
9. Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Assembly
What is the typical lead time for PCB assembly?
Lead times can vary based on the complexity of the project and the manufacturer, but typical turnaround times range from a few days to several weeks.
How can I ensure the quality of my PCB assembly?
Utilizing precision instruments, adhering to design principles, and implementing robust quality control processes are key to ensuring high-quality PCB assembly.
What are the most common challenges in PCB assembly?
Common challenges include component misalignment, inadequate solder joints, and difficulties in testing and inspection.
How does automation impact PCB assembly?
Automation increases speed, consistency, and accuracy in PCB assembly, allowing for higher production rates and reduced human error.
What is the role of inspection in PCB assembly?
Inspection is crucial for identifying defects and ensuring that the assembled PCB meets the required quality standards before reaching the market.
10. Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of PCB assembly requires a comprehensive understanding of the process and the tools involved. With the integration of precision instruments, manufacturers can enhance the quality and reliability of their products. By implementing best practices, investing in employee training, and staying abreast of emerging technologies, companies can ensure their PCB assembly processes remain competitive in an ever-evolving industry. The future of PCB assembly looks promising, with advancements paving the way for even more efficient and accurate production methods.
This article serves as an extensive guide for both newcomers and seasoned professionals in the electronics manufacturing industry. By focusing on precision and quality, we can continue to meet the increasing demands of technology while maintaining high standards in PCB assembly.
Related news